Niagen® Research: The Latest Science

Niagen® Research: The Latest Science
Niagen® is a patented form of nicotinamide riboside (NR), a rare form of
You need vitamin B3 for proper cellular metabolism and repair. It helps convert the food you eat into vital energy and helps your cells defend against free radical damage.
But NR takes the benefits of vitamin B3 to the next level. Often mistakenly dubbed the “anti-aging” vitamin, NR is heralded for its compounding benefits of improving the way you age.
How does NR improve the way you age?
Under the microscope, you’ll see that NR converts into a compound called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+).
NAD’s primary role is to support the function of the mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell. And the health of your mitochondria and the way you age are intrinsically tied.
A review published in the Journal of Signal Transduction illustrates speculation that cumulative damage to mitochondria caused by free radicals is one of the root causes of ageing.
In fact, a team of researchers proposed mitochondrial dysfunction as one of the nine hallmarks of aging.
NR has the ability to support NAD+ levels to better support the health and function of your mitochondria.
Why is Niagen® better than other forms of NR?
NR has several variations out in the market, but Niagen® is the only patented form of NR. You can’t entirely trust other non-patented forms as they have not achieved the same regulatory standard.
Niagen® is the only form of NR that has been successfully notified to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It’s been successfully reviewed twice under the FDA’s New Dietary Ingredient Notification (NDIN).
It also has achieved regulatory acceptance in Canada, the European Union, and Australia under its already outstanding resume.
Explore the 12 human studies behind Niagen®.
Niagen® has been the subject of 12 human studies, nine of which demonstrate that it effectively supports NAD+ levels. Take a closer look at each of them below:
1st Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
Nature Communications, 2016
Study Design:
A randomized, double-blind, three-arm crossover trial was conducted. Subjects consisted of 12 healthy men and women between the ages of 30 and 55. The subjects were given 100mg, 300mg, and 1000 mg of NR.
Study Results:
The study reports that single oral doses of 100mg, 300mg, and 1000mg of Niagen® can effectively elevate NAD+ levels.
2nd Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
PLOS One, 2017
Study Design:
A non-randomized, open-label trial was conducted. Subjects consisted of eight healthy men and women between the ages of 21 and 50. The subjects were given 250mg of NR on days one and two, then gradually administered higher doses each subsequent day after. On days seven and eight, the study administered a peak dose of 1000mg twice daily.
Study Results:
The study reported oral administration of Niagen® to be well-tolerated in humans with no adverse effects.
3rd Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
Nature Communications, 2018
Study Design:
A randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial was conducted. Subjects consisted of 60 healthy men and women between the ages of 55 and 79. Subjects received either 500mg NR twice per day or a placebo for six weeks.
Study Results:
The study reported Niagen® supplementation is well-tolerated and effectively supports NAD+ in a group of healthy middle-aged and older adults with no adverse events or side effects attributable to NR.
4th Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2018
Study Design:
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study was conducted. Subjects consisted of 40 healthy, sedentary men with a body mass index (BMI) > 30kg/m2 between the ages of 40 and 70. Subjects received either 1000mg of NR per day or a placebo for 12 weeks.
Study Results:
Twelve weeks of NR supplementation in doses of 2000mg per day is well tolerated.
5th Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2019
Study Design:
Same trial as 4th study.
Study Results:
NR supplementation for 12 weeks did not affect fasting or improve glucose handling.
6th Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
The Journal of Physiology, 2019
Study Design:
Same trial as 4th study.
Study Results:
NR supplementation for 12 weeks increased concentrations of NAD-derived metabolites detected in the urine. NR supplementation did not change NAD metabolite levels in human skeletal muscle.
7th Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
Scientific Reports, 2019
Study Design:
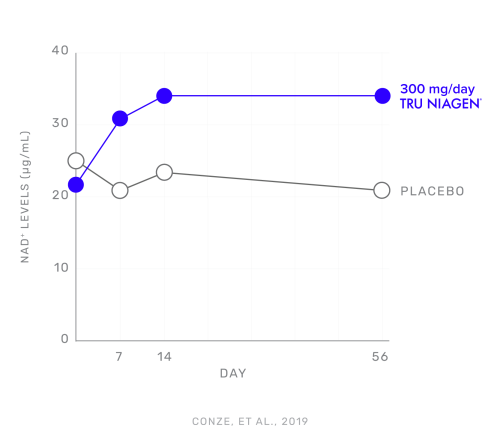
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study was conducted. Subjects consisted of 140 healthy, overweight male and female participants between the ages of 40 and 60. Subjects received either 100mg, 300mg, or 1000mg of NR per day or placebo for eight weeks.
Study Results:
NR consumption of 100mg, 300mg, and 100mg significantly increased whole blood NAD+ levels by 22%, 51%, and 142%, respectively, after two weeks. These levels were also maintained throughout the remainder of the study.
8th Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
Cell Reports, 2019
Study Design:
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study was conducted. Subjects consisted of 12 aged (median age of 75 years) and marginally overweight, healthy men. Subjects received either 1000mg per day or a placebo for 21 days.
Study Results:
NR increased human skeletal muscle NAAD, a sensitive marker of increased NAD+ metabolism.
9th Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2020
Study Design:
A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover study was conducted. Subjects consisted of 113 healthy, overweight or obese men and women. Subjects received either 1000mg of NR per day or a placebo for six weeks.
Study Results:
Similar to the previous study, NR supplementation significantly increased markers of enhanced NAD+ metabolism in human skeletal muscle.
10th Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
Molecular Systems Biology, 2020
Study Design:
A 5-day calibration study with nine healthy male subjects was conducted. Subjects received NR, L-carnitine tartrate, N-acetyl-L-cysteine, and L-serine on separate days and a combined “cocktail” of all the substances on another day.
After 21 months, a 1-day control study with ten male subjects was conducted to compare results.
Study Results:
Mathematical modeling results showed this “cocktail” of supplements increased fat metabolism, decreased glucose metabolism, and increased synthesis/turnover of NAD+, carnitine, and glutathione.
11th Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2020
Study Design:
An ex vivo and pilot study was conducted. Participants were put on escalating doses of NR, 250mg 2x a day for Day 1, 500mg 2x a day for Day 2, and 1000mg 2x a day from Day 3 and onward for 5 to 9 days.
Study Results:
The study showed NR increased whole blood NAD+ levels and the mitochondrial respiration rate of white blood cells.
12th Published Human Niagen® Study
Published In:
The Journal of Physiology, 2021
Study Design:
Eight young male participants received either a placebo or 1000mg of NR per day for one week. Participants were then subjected to exercise to exhaustion on a bicycle ergometer.
Study Results:
One week of NR supplementation did not alter whole-body metabolism or skeletal muscle signal transduction pathways implicated in the mitochondrial adaptation to endurance exercise.
The science behind Niagen® continues to grow.
There are more than 45 ongoing studies involving Niagen®, according to the clinicaltrials.gov database and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry. The ever-growing research shows how much the world’s leading researchers find plenty of promise with Niagen® and its unique benefit of raising NAD+ levels efficiently.



 .
.